Every time your customers make an online payment, they trust that their sensitive data won’t end up in the wrong hands. But what if it did? With cybercriminals using AI and launching direct attacks on payment systems, securing financial transactions has become a high-stakes challenge for businesses worldwide.
In the first half of 2023, around 48.77 billion card payments were made with EU/EEA-issued cards, of which an average of 7.31 million were fraudulent. If digital payments are your business’s bread and butter, payment tokenization is a technique you might want to look at, to combat payment fraud and protect customers.
Understanding Payment Tokenization
Payment fraud occurs when attackers access sensitive payment information—such as credit card details—and use it for unauthorized transactions. When payment data is stolen or intercepted during a transaction, fraudsters can use it to make unauthorized purchases, or sell it on the dark web to other bad actors looking to do the same.
Payment tokenization is a security technique that protects against this kind of fraud. It replaces sensitive payment information—such as credit and debit card numbers or primary account numbers (PANs)—with random character strings called tokens, rendering intercepted data useless to attackers.
This process protects card payment data during transactions, as these meaningless tokens are transmitted instead of the actual payment details. Attackers who manage to intercept these tokens cannot use them to make fraudulent purchases, enabling businesses to provide a secure and seamless payment experience.
How does Payment Tokenization Work?
Tokens are created using robust cryptographic algorithms, which replace real payment data with randomly generated character strings. The tokens are then stored in a separate database, known as a token vault; this database is highly secure, and is typically hosted by trusted third-party providers known as ‘token service providers’ (TSPs). The tokens are stored along with the original payment data to which they refer, and a lookup table associates each token with its corresponding original data.
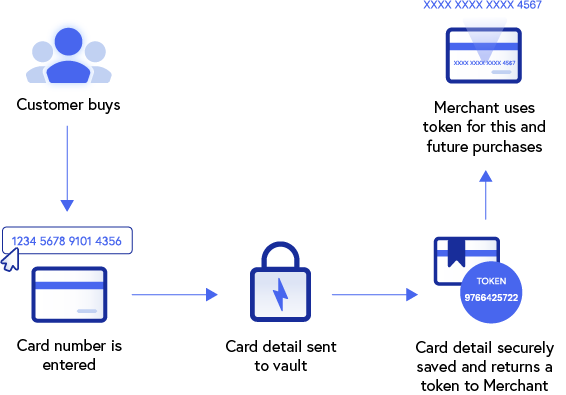
The token is then sent to the card issuer to authorize this transaction. The verified token is returned to the TSP and sent to the merchant to complete the payment. The merchant can store the token for future transactions from that customer, such as recurring payments, refunds, or enabling one-click payments.
There are three types of tokenization:
- Network tokens are issued by a TSP and are linked to a specific device, replacing PANs at every stage of the transaction
- PCI tokens protect the PANs held by merchants, payment processors, and others and are stored in the secure token vaults of TSPs. These tokens are specifically used to reduce the scope of PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance requirements
- Digital wallet tokens power digital wallets like Google Pay and Apple Wallet and store sensitive data such as PANs, CVVs, and expiry dates
What’s the Difference Between Tokenization and Encryption?
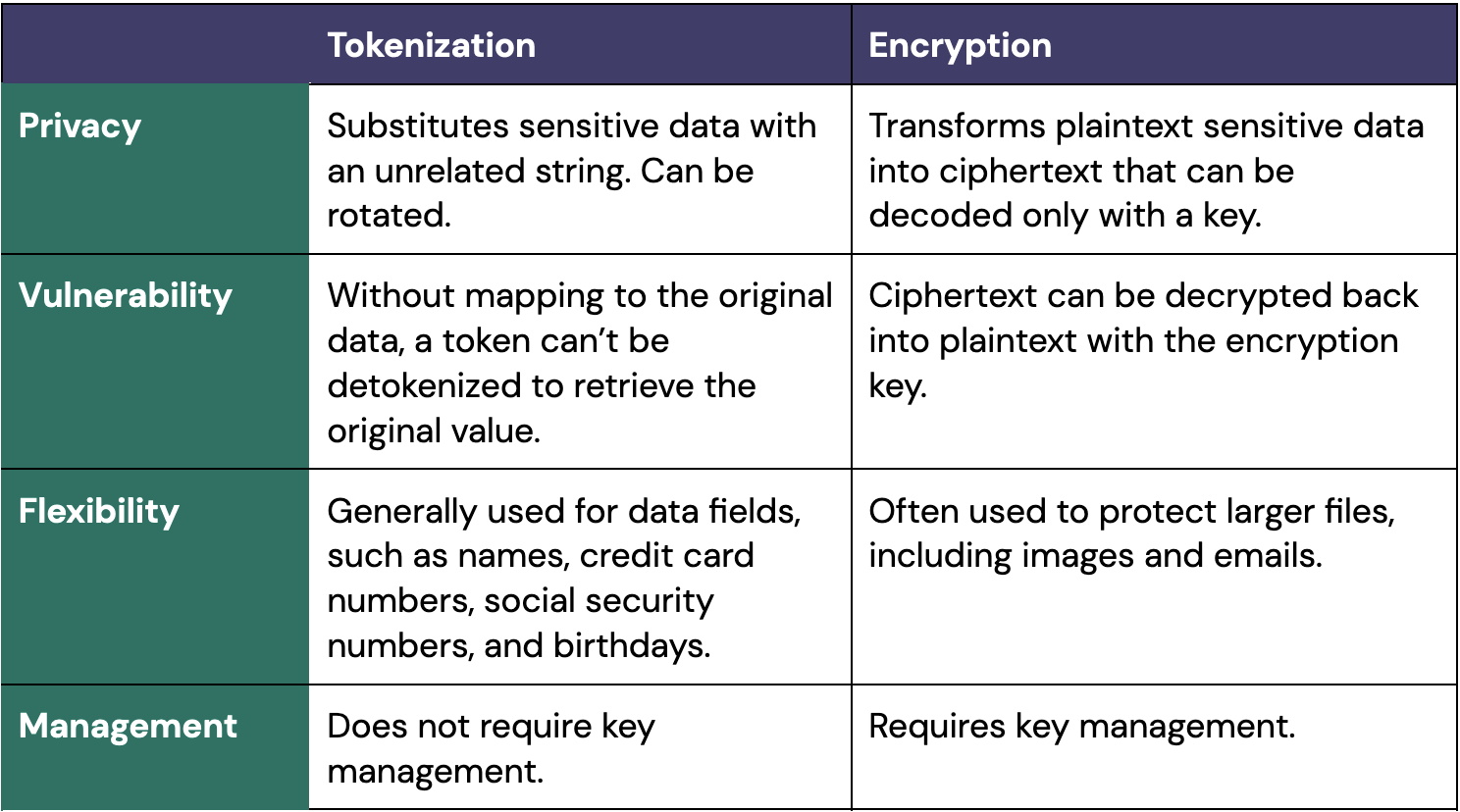
Tokenization and encryption are closely related concepts and aim to achieve similar goals. Tokenization can replace sensitive data completely, whereas encryption transforms it and can be reversed using a decryption key. Tokens are stand-ins for the actual data, whereas encrypted data is a modified form of the original data.
How is Tokenization Used in the Real World?
- Point of Sales systems in physical stores use tokenization to transform PANs for payment processing;
- Digital wallets use tokenization to secure transactions from smartphone apps and other digital devices;
- eCommerce businesses rely on tokenization to facilitate one-click transactions and to offer a more convenient, secure online experience;
- Subscription services use tokens to process recurring payments;
- Platforms and marketplaces use payment tokenization to enhance their security and streamline data management for millions of customers;
What Will Payment Tokenization Mean for Information Security?
Payment tokenization is increasingly essential for information security, particularly given the rising numbers of digital transactions, mobile payments, and evolving cyber threats. Here’s why it is expected to have a transformative impact:
1. Data Breaches
Given the large amounts of sensitive data it handles, the financial sector is uniquely exposed to cyber risk. As of 2024, the average data breach cost in the United States amounted to $9.36 million.
In this environment, protecting sensitive payment data is critical. Payment tokenization renders primary account numbers (PANs) and other sensitive payment details useless for fraudulent activities by replacing them with secure, non-sensitive tokens during transactions.
Payment fraud is not limited to financial services. Fraudsters often target businesses that store payment card data or process payments without sufficient security measures, such as encryption or tokenization. E-commerce fraud, for instance, is particularly prevalent.
2. Compliance Requirements
Payment tokenization significantly reduces merchants’ exposure to sensitive payment data. It eliminates the need to store original cardholder data, keeping transactions secure and simplifying compliance with PCI DSS and other data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
By reducing the scope of compliance audits and limiting the exposure of sensitive data, tokenization lowers the costs and risks associated with regulatory violations, such as fines, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Beyond meeting regulatory obligations, tokenization strengthens customer trust and demonstrates a proactive commitment to data protection.
3. Contactless Payments and IoT Transactions
As contactless payments and IoT-based transactions grow in adoption, they introduce new attack vectors for cybercriminals. By isolating sensitive data from the transaction process, payment tokenization significantly reduces the attack surface while ensuring convenience and scalability for emerging technologies. While tokenization primarily defends against interception attacks during transactions, other techniques like encryption cover other parts of the payment flow.
Protect Against Payment Fraud Beyond Tokenization
While tokenization is effective, it does not eliminate all payment fraud risks. There are several best practices that your organization needs to adopt to be fully fraud-protected, which include:
1. Adaptive Authentication
Adaptive authentication is an advanced fraud prevention approach that tailors authentication requirements based on risk factors, such as user behavior, device characteristics, location, and transaction context.
Adaptive authentication can identify and mitigate fraudulent activity without compromising the user experience by analyzing multiple data points. Geolocation, Multi-factor Authentication, behavioral biometrics, and other contextual data are all examples of adaptive authentication.
2. Real-Time Threat Intelligence
Real-time threat intelligence uses the latest data and insights on emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and attack tactics to quantify cyber risk and support proactive defenses. By leveraging real-time data feeds and analytics, you can detect suspicious activities, reducing the likelihood of successful payment fraud.
You should integrate real-time threat intelligence into your security infrastructure to maximize its potential. Connecting threat intelligence feeds with your SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) enables quicker identification of anomalies.
3. Token Lifecycle Management
Token lifecycle management ensures the secure and automated workflow of payment tokens’ lifecycle—from creation and use to expiration and destruction. To effectively manage tokens’ lifecycles, businesses should implement a combination of secure token management systems and cryptographic tools such as APIs, SDKs, and token management platforms to ensure that tokens are used as intended.
4. Website Spoofing Protection
What if, instead of stealing payment data by intercepting transactions, attackers could simply trick users into handing over their sensitive information? That’s the essence of fake websites. These deceptive sites mimic legitimate ones to collect sensitive data—such as payment details—by misleading users into entering their information.
While payment tokenization safeguards transactions within secure payment systems, it doesn’t address risks from external threats like phishing and fake websites. Memcyco’s solutions fill this gap by providing real-time protection against digital impersonation and ATO (account takeover) fraud.
Using proprietary algorithms, Memcyco delivers unmatched real-time visibility into attacks, attackers, and each victim. This empowers businesses to stop fraud at its source, mitigate damage, and ensure their customers’ payment details remain secure.
5. Monitor Transactions with Behavioral Analytics
Behavioral analytics plays a crucial role in identifying payment fraud by analyzing patterns in customer behavior. Businesses can detect and prevent fraudulent activities by observing typical behaviors and flagging deviations from the norm.
Behavioral analytics involves tracking how customers interact with payment systems—such as their login behavior, spending patterns, device usage, and transaction characteristics—across various touchpoints.
Providing a Holistic Payment Security Strategy
Payment tokenization is critical in securing payment data by replacing sensitive information with non-sensitive tokens. However, when it comes to website spoofing, where fraudsters create fake websites to steal payment details, tokenization alone is not enough to protect consumers. In these cases, Memcyco offers a vital layer of security by detecting phishing websites and alerting businesses when their customers visit fraudulent sites. This keeps customer accounts secure while scams remain active and after they’re taken down.
Memcyco also leverages decoy data, replacing real customer data, if customers unknowingly enter it on a fake site, with artificial data that fraudsters will assume is real. This prevents fraudsters from accessing legitimate payment details, even when users are on an impersonating website. By proactively identifying fake sites and neutralizing data theft attempts, Memcyco is the first line of defense against fraud that tokenization cannot address. Learn more here.