Imagine this: Eagerly awaiting a limited-edition sneaker release, Tyler frequently checked his phone for updates from SneakPeak Elite. One day, an email announced an early-bird sale for loyal customers. Following the link, Tyler found a site identical to SneakPeak Elite and confidently made his purchase. However, by Monday, unauthorized bank transactions revealed the truth: the phishing email and spoofed website were part of a sophisticated Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack—and now a hacker had Tyler’s financial details.
MitM attacks, once thought to be limited to the realms of tech-savvy criminals, have become alarmingly mainstream. Recent reports have indicated that 19% of successful cyber attacks are MitM attacks, and over $2 billion worldwide was lost due to these schemes. If you’re involved in the digital realm of any e-commerce, fintech, or online payment company, understanding and thwarting these threats isn’t just a recommendation—it’s an absolute necessity.
In this post, we dive into the midst of Man-in-the-Middle attacks. We’ll look into how they work, the different types, and their risks—and provide eleven preventive measures you need to implement now.
What are Man-in-the-Middle attacks?
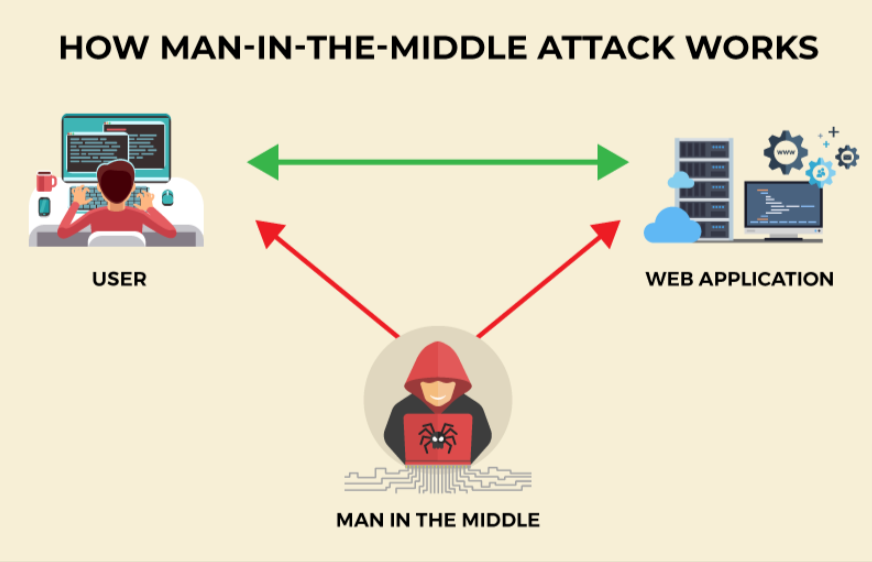
MitM attacks, at their core, involve unauthorized interception. A malevolent actor secretly relays and possibly alters the communication between two parties, making each believe they’re talking directly to each other. One widespread misconception is that MitM attacks only target insecure or shady websites. In reality, even reputed sites with robust security measures can fall victim, especially if the end user’s environment is compromised.
While individual users can indeed be affected, the most enticing targets for MitM attackers are often businesses, government organizations, and especially the burgeoning e-commerce and fintech sectors. The stakes in these sectors are high: financial transactions, sensitive data transfer, and confidential communications.
So, why should everyone be concerned? Because in an era where digital trust is paramount, a single successful MitM attack can lead to significant financial losses and erode the trustworthiness of digital platforms. In the blink of an eye, both reputations and revenues can vanish. Every internet user, whether a casual browser or a digital enterprise, must recognize and combat this insidious threat.
How do Man-in-the-Middle attacks work?
The mechanics of a MitM attack can be likened to an eavesdropper stealthily intercepting a whispered conversation, sometimes manipulating it for their gain. The attacker places themselves between the network and the victim, intercepting and relaying messages between them, all while staying undetected. This can be done through various means, including WiFi eavesdropping or leveraging compromised routers.
Take, for example, this scenario at a popular coffee shop: An unsuspecting patron logs onto what they believe is the shop’s free WiFi. In reality, they’ve connected to a rogue hotspot set up by the attacker, lurking nearby. When our patron logs into their bank account or enters credit card details for a purchase, that sensitive information passes directly through the attacker’s system, allowing them to capture and exploit it.
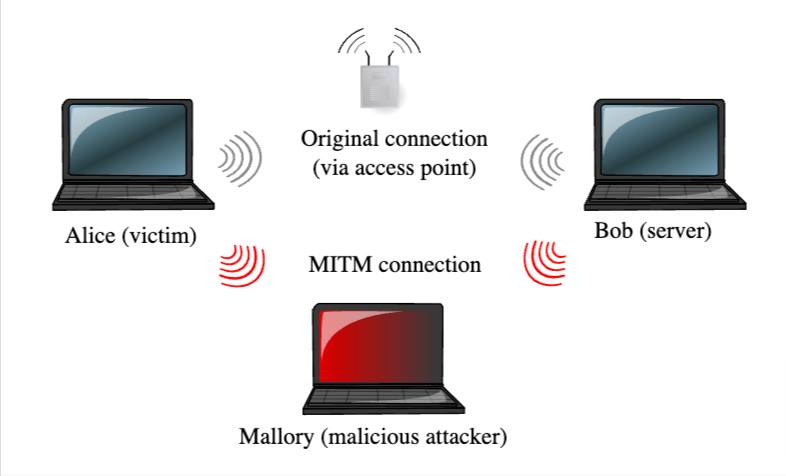
This modus operandi showcases how MitM attacks, blending technical prowess with social engineering, can exploit even the most routine of our digital behaviors.
The Different Types of Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
In the complex cybersecurity landscape, multiple methods can initiate a MitM attack—each distinct, yet equally menacing.
ARP Spoofing
In ARP spoofing, the attacker sends deceptive ARP messages to map an IP address to a different MAC address. The attacker can control and monitor the data exchanged between two systems on a mutual network.
Cross-Site Request Forgery
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is an attack where the attacker deceives a user into performing an unintentional action on a web platform. They can exploit this to modify user settings or act on their behalf.
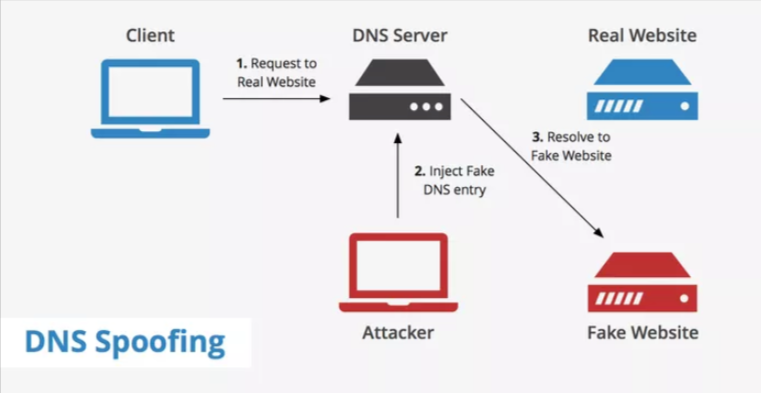
DNS Spoofing
Here, the attacker alters the DNS server configurations, directing users to illegitimate spoofed or mirrored websites that often closely resemble their legitimate counterparts.
Eavesdropping
Also known as communication interception, this technique involves the attacker discreetly observing the active communication between two systems, allowing them to glean and, potentially, alter the transmitted information.
WiFi Man-in-the-Middle Attack
A WiFi MitM attack occurs when an attacker discreetly intercepts the communication between devices in a WiFi network. They exploit weak security, position themselves in the communication pathway, and have the ability to oversee, alter, or introduce new data.
Packet Sniffing
In this method, attackers capture and analyze data packets moving across a network. This provides them an opportunity to view or alter data that’s in transit.
Rogue Access Points
This attack is when an attacker sets up a counterfeit network access point. When users unknowingly connect to this, the attacker gains the capability to oversee and manipulate the data users send or receive.
Session Hijacking
In session hijacking, the attacker intrudes on an ongoing session between two parties. Inserting themselves in the middle, they can monitor, modify, or terminate the session.
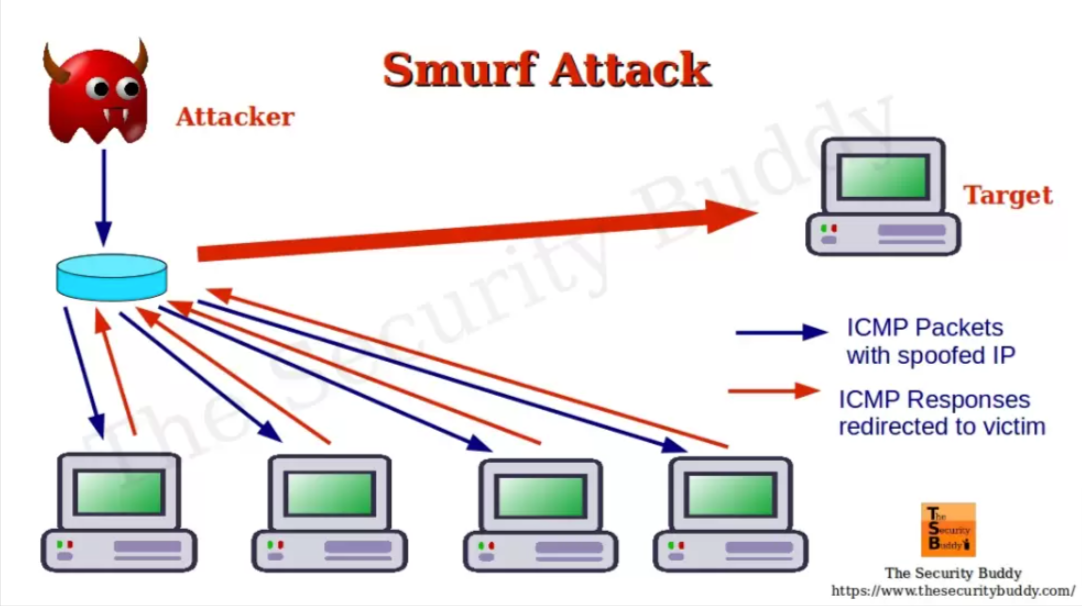
Smurf Attack
During a Smurf attack, the attacker overwhelms a target with excessive traffic, masquerading the source IP address of packets. The aim is to oversee and alter the data being exchanged.
SSL Stripping
SSL stripping involves the attacker’s attempt to downgrade a secure HTTPS connection to an unsecured HTTP one, offering a clear view into the data exchange and an opportunity for tampering.
Risks of Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
MitM attacks strike at the very core of cybersecurity’s triad: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Let’s delve into how.
- Threat to Confidentiality – MitM attackers can access confidential information like login credentials, credit card numbers, and other sensitive personal details by intercepting data mid-transit. The data breach’s repercussions are vast, ranging from identity theft to unauthorized financial transactions.
- Integrity at Risk – An attacker doesn’t just stop at reading the data. They can modify it, inject malicious content, or alter transaction details. Imagine the chaos when financial details are tweaked, or a command is changed in an industrial setting.
- Availability Concerns – While not as common, some MitM attacks can divert traffic or overload systems, causing disruptions or rendering services unavailable. This can cripple operations, especially in sectors like e-commerce or fintech, where continuous availability is paramount.
- Reputational Harm – In terms of damages, besides the immediate financial loss, there’s the prolonged sting of reputational harm which can lead to loss of sales and revenue. Companies spend years building trust; a single MitM attack can dismantle that.
Understanding these risks underscores the urgent need for proactive defense measures.
11 Practices to Prevent Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
MitM attacks pose a serious threat to companies and their clientele. Fortunately, there are several strategies you can implement to defend against these invasive interceptions:
1. Integrating Memcyco’s Solution
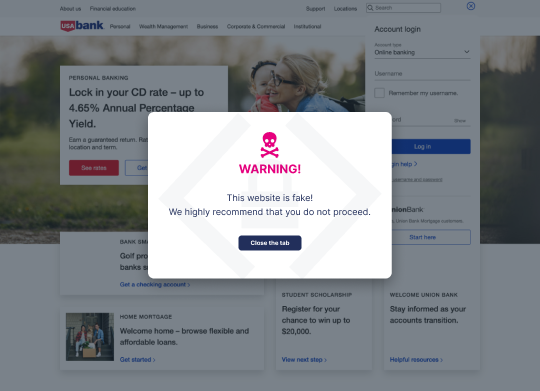
MitM attacks frequently rely on website spoofing, convincing users they’re on the legitimate site when they’re not. Memcyco offers an unparalleled defense against the dangers of spoofed website, with a unique set of features:
- Real-time Alerts: Issues a Red Alert in real-time to your customers who visit a fake site.
- Visibility: Provides you with full details of the attack to ensure complete visibility.
- Watermark: Includes an unforgeable, customizable watermark that marks your sites as legit.
- Agentless: your customers don’t need to install anything or register anywhere.
- Easy Implementation: Simply add a few lines of code, and start realizing value within hours.
By employing Memcyco’s agentless, out-of-the-box solution, companies are safeguarded during the critical window of exposure, the time a fake website goes up until it’s taken down. Companies benefit from less direct financial losses and enhance trust among their customers, fostering better relationships and safeguarding their reputation. Memcyco ensures compliance (with regulations fast approaching), and assures less data leakage and privacy issues, which otherwise may lead to account takeover and ransomware attacks.
2. HTTPS and Secure Connections
Ensuring your website is served over HTTPS instead of HTTP means the data is encrypted and significantly more challenging for hackers to intercept. Always check for the green padlock symbol in the address bar, which affirms a secure connection.
3. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
VPNs create an encrypted connection from a user’s device to the network. Routing traffic through a secure virtual tunnel makes interception remarkably challenging for potential attackers.
4. Public Key Pinning
This process involves associating a host with their expected public key, ensuring that the public key remains the same during subsequent connections, thus reducing the risk of MitM attacks during SSL/TLS handshakes.
5. Regular System Updates and Patches
Software developers frequently release updates to address known vulnerabilities. Regularly updating your systems and applying patches can protect you from attackers exploiting these known vulnerabilities.
6. Data Encryption
Beyond secure connections, ensure that sensitive data, both in transit and at rest, is encrypted. This guarantees that the data remains unintelligible to the intruder even if intercepted.
7. Strong Authentication Protocols
Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA). By requiring multiple forms of verification, it becomes immensely challenging for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they have intercepted some credentials.
8. Network Segmentation
Divide your network into multiple segments, ensuring that if one segment is compromised, it doesn’t automatically jeopardize the entire network.
9. Employee Awareness and Training
Most cyber-attacks exploit human errors. Regular cybersecurity awareness training sessions can ensure that employees recognize suspicious activities and are equipped with best practices to prevent inadvertent security lapses.
10. Monitoring Network Traffic
Employ network monitoring tools to observe and analyze traffic for unusual patterns or suspicious activities. Immediate alerts can be set up for potential threats, ensuring timely interventions.

11. Secure WiFi Networks
Ensure your company’s WiFi is secured using robust encryption methods, like WPA3, and avoid using public WiFi for confidential transactions without a secure VPN.
Preventing MitM Attacks is Imperative for Your Organization
In the digital realm, Man-in-the-Middle attacks loom large, threatening businesses and customers with breaches in confidentiality, integrity, and availability. From ARP Spoofing to WiFi Eavesdropping, the methods are diverse, but the risks—financial, reputational, and operational—are universal.
MitM attack prevention isn’t merely a good practice; it’s imperative. At the heart of this defense strategy is Memcyco’s innovative solution, bridging the protection gap with real-time alerts, impeccable visibility, and unfaltering watermark verifications.
Ready to fortify your digital frontiers? Don’t wait for the next threat to strike. Experience Memcyco in action by trying a demo today.