SEO Poisoning Protection
Disarm SEO poisoning, reclaim your revenue
SEO poisoning protection that’s fast, automated and scalable.
How SEO poisoning starts and ends

Phase 1
SEO poisoning attack preparation
Bad actors study your site code as part of SEO poisoning attack preparations.

What if you could
Detect website reconnaissance attempts in real time, before SEO poisoning attacks even start.

Phase 2
Fake site creation
After studying your site code, bad actors create and launch impersonating websites that look just like yours.

What if you could
Be instantly alerted when lookalike URLs are registered, and when they go live.
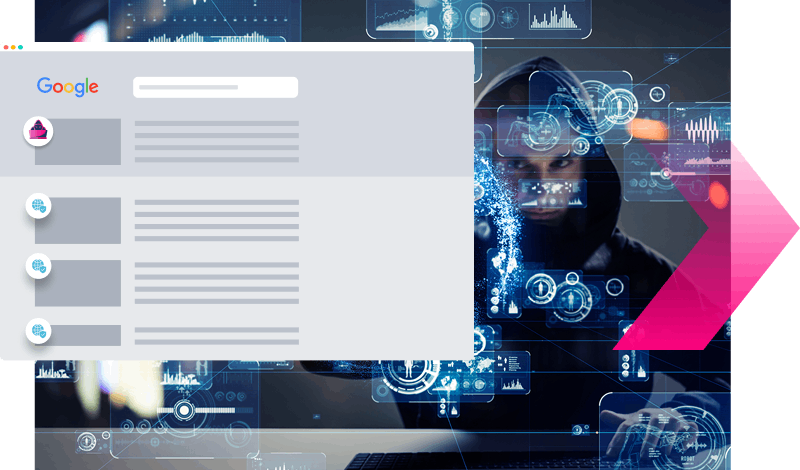
Phase 3
Organic promotion of fake sites
Once live, fraudsters use blackhat SEO techniques like keyword stuffing to organically promoting their fake site ranking over yours.
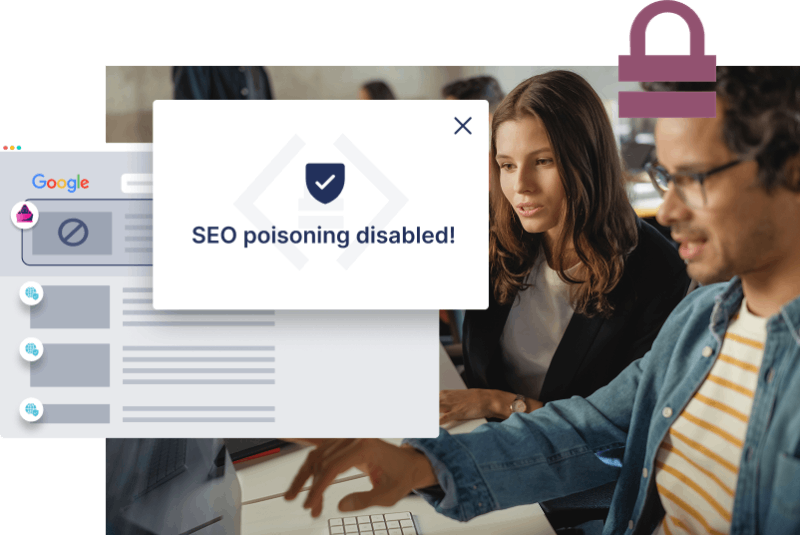
What if you could
Automatically disable SEO poisoning and downgrade offending websites’ ranking to reclaim your search engine results?
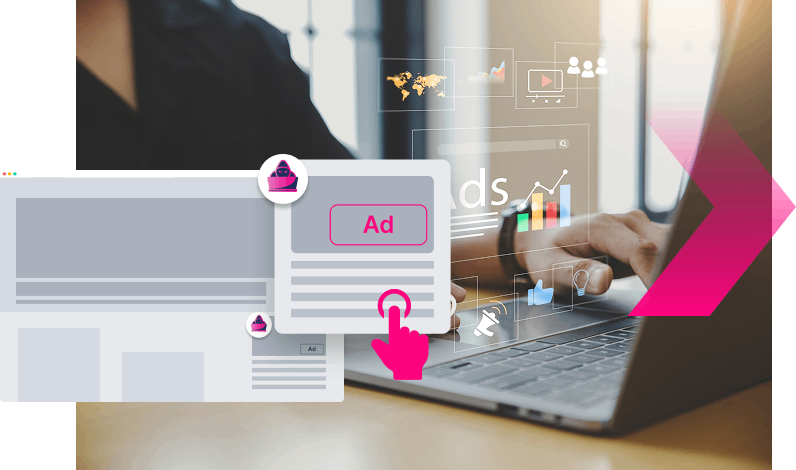

Paid promotion of fake sites
Fraudsters may also use pay-per-click (PPC) techniques to promote their fakes and steal traffic using Search or Display ads.

What if you could
Automatically disable impersonating websites promoted in search results using fake paid ads?

The business impact
You may not even realize you’re losing revenue, as fake sites fulfill orders with counterfeit goods and competing fake ads increase your PPC campaign cost.

What if you could
Shield revenue, brand equity and customer acquisition cost efficiency from SEO poisoning and malicious paid ads?
Disarm SEO poisoning, without the heavy lifting
With Memcyco
Instant visibility and disarming of SEO poisoning threats as they happen
Always-on, without need for manual intervention
Effortless and effective without burdening IT teams
Without Memcyco
Time-consuming, prone to human error, and slow to detect threats
Reactive, prone to blind spots, requires regular updates
Labor-intensive, potential gaps in protection, high overheads
Crush ATOs earlier, and keep them crushed longer
Discover why global brands replace their previous solution with Memcyco

Scalable SEO poisoning protection
Downrank
sucess rate
93%
Downrank process
starts in under
72 hrs
Downrank long term
effectiveness
100%
Already crushing SEO Poisoning?
Solve more

Man in the Middle (MiTM) Protection




SEO poisoning scams

Credential Stuffing



Fake e-shops, purchase scams, gift card scams

Get a Custom Demo
See it in action and discover why others switch to Memcyco
Get a demo to learn how Memcyco customer :
-
Identify individual scam victims in real-time
-
Predict and preempt ATO incidents
-
Deceive threat actors
Frequently asked questions
What is SEO poisoning and how does it work?
SEO poisoning is a cyberattack where malicious actors manipulate search engine rankings to push compromised or fake websites to the top of search results. These websites often contain malicious content, such as malware or phishing traps. Attackers use techniques like keyword stuffing, cloaking, and link farms to make their malicious pages appear relevant to popular search terms. Once users click on these results, they may be redirected to malware-laden websites or phishing pages designed to steal personal information, credentials, or financial data.
What kind of vulnerabilities do SEO poisoning attacks exploit?
SEO poisoning primarily exploits vulnerabilities in search engine algorithms, often taking advantage of weaknesses in how search engines rank and categorize content. Additionally, these attacks exploit users’ trust in search engines, as many users assume the top search results are legitimate. Another vulnerability arises from poor website security practices, such as insufficient protection against drive-by downloads or cross-site scripting (XSS), which attackers may exploit once users are redirected to malicious websites.
How does SEO poisoning impact search engine optimization (SEO) efforts for legitimate websites?
SEO poisoning can severely impact legitimate websites by crowding search results with malicious or irrelevant content, which pushes legitimate pages down in rankings. This reduced visibility can lead to a significant drop in organic traffic. Additionally, legitimate websites may suffer reputational damage if users mistakenly associate them with the fraudulent sites. Moreover, SEO poisoning can create a competitive disadvantage, particularly in industries where search rankings are a key driver of business.
What methods are commonly used by attackers to carry out SEO poisoning?
Attackers typically use several techniques to carry out SEO poisoning. These can include:
Keyword stuffing: Overloading pages with popular keywords to manipulate search engine rankings.
Cloaking: Serving different content to search engine crawlers than to users, tricking the search engine into indexing a seemingly legitimate page.
Backlink manipulation: Creating link farms or purchasing backlinks from compromised websites to boost the ranking of the malicious page.
Hijacking legitimate websites: Injecting malicious code into legitimate, high-traffic websites, so when users click on the site, they are redirected to a malicious domain.
How can SEO poisoning attacks be identified by security teams?
Identifying SEO poisoning attacks involves several strategies:
- Analyzing referral traffic: Suspicious spikes in traffic from search engines could indicate that SEO poisoning is redirecting users to or from a compromised website.
- Monitoring website rankings: A sudden drop in search rankings or a spike in similarly named fraudulent websites in search results may indicate an ongoing SEO poisoning attack.
- Checking for suspicious redirects: Regularly analyzing website access logs and search queries can reveal malicious redirects that may be indicative of SEO poisoning.
What industries are most commonly targeted by SEO poisoning?
Industries that rely heavily on online search traffic and customer engagement via websites are frequently targeted. This includes e-commerce, financial services, healthcare, and hospitality. These industries are often targeted because attackers know that compromised websites can lead to significant financial gain, either through direct theft or by compromising sensitive personal information. Additionally, websites in these industries typically have a large, diverse user base, making them lucrative targets for SEO manipulation and fraud.
What are the potential consequences for users who fall victim to an SEO poisoning attack?
When users fall victim to SEO poisoning, the consequences can be severe. They might unknowingly download malware, such as ransomware or keyloggers, onto their devices, which can lead to data theft or financial loss. Additionally, users may be directed to phishing sites that mimic legitimate businesses, resulting in the exposure of sensitive information, such as login credentials, Social Security numbers, or credit card details. In some cases, SEO-poisoned websites might perform drive-by downloads, automatically installing malware without any user interaction.
How can search engines protect against SEO poisoning?
Search engines combat SEO poisoning by continually refining their algorithms to better detect and penalize malicious sites. Some common measures include:
- Improving content analysis: Search engines can use machine learning to analyze website content for patterns typical of SEO poisoning, such as unnatural keyword density or irrelevant backlinks.
- Increased scrutiny of backlinks: Algorithms are now designed to evaluate the quality and relevance of backlinks to prevent link farm manipulation.
- Enhanced real-time monitoring: Search engines can employ bot detection and other monitoring techniques to spot unusual search behavior or spikes in keyword usage that might indicate an SEO poisoning attack.
What measures can businesses implement to defend against SEO poisoning?
Businesses can protect themselves from SEO poisoning by:
- Regularly auditing website security: Implementing measures like SSL certificates, web application firewalls (WAFs), and content security policies (CSPs) can help prevent their site from being hijacked.
- Monitoring keyword rankings: Businesses should continuously track their search engine rankings and investigate sudden changes that may indicate SEO manipulation.
- Utilizing monitoring tools: Real-time security tools can detect unusual traffic patterns or sudden spikes in search traffic, which may point to SEO poisoning attempts.
How can businesses recover from an SEO poisoning attack?
Recovery from an SEO poisoning attack involves multiple steps:
- Identifying and removing malicious content: Businesses need to thoroughly scan their website for any injected malware or compromised scripts and remove them.
- Improving SEO hygiene: Post-attack, businesses should audit their SEO practices and remove any low-quality backlinks or suspicious content that may have been introduced.
- Strengthening security protocols: To prevent future attacks, businesses should bolster their security with measures like multi-factor authentication (MFA), stronger access controls, and real-time monitoring of search results and web traffic.
- Notifying affected users: If users were compromised, businesses should alert them promptly, providing steps they can take to secure their accounts or recover lost data.