Imagine your finance team receives an urgent email that appears to be from a trusted supplier, notifying them of an unexpected change in bank account details for an upcoming payment. The email looks professional, is detailed, and contains all the expected business formalities. Without hesitation, the team processes the payment to the new account. Days later, the actual supplier contacts you about the overdue invoice. Only then do you realize the email was fraudulent—and the funds have been transferred to a scammer’s account.
This scenario is a classic example of Authorized Push Payment (APP) fraud, a rapidly growing cybercrime tactic that targets businesses and individuals by exploiting their trust in routine transactions. The cumulative monetary loss from APP fraud across major world markets is expected to reach $6.8 billion USD by 2027. This alarming figure highlights the sophisticated nature of these scams and the significant financial damage they can cause to individuals and businesses alike.
As APP fraud continues to evolve, it’s crucial for businesses to understand this threat and implement effective measures to protect their customers and reputations.
What is APP fraud?
Authorized Push Payment (APP) fraud is a sophisticated cybercrime where fraudsters manipulate victims into authorizing a payment to the fraudster’s account.
APP fraud uses social engineering techniques to deceive individuals and businesses into believing they are making legitimate payments. The fraudster often impersonates a trusted entity, such as a bank, supplier, or senior executive within the victim’s company, to gain credibility and convince the victim to transfer funds.
The urgency to address APP fraud has never been greater. As businesses increasingly depend on digital transactions, the opportunities for fraudsters to exploit vulnerabilities have increased. The rise of remote work and the global use of online banking have expanded the attack surface, making it easier for criminals to execute these scams.
APP fraud can cause devastating financial and reputational damage, leading to significant monetary losses and eroding trust in digital payment systems. For businesses, the stakes are high—not only must they safeguard their assets, but they also bear the responsibility of protecting their customers and partners from falling prey to these schemes. There are also regulatory concerns, and some countries (such as the UK) now require payment service providers to reimburse victims. Proactively addressing APP fraud is essential to maintaining cybersecurity and digital trust.
How does APP fraud work?
APP fraud relies on the fraudster’s intricate planning to set a trap, which requires two essential elements.
First, the fraudster must create a scripted bogus offer based on an impersonation pretext—a fake storyline to entice potential victims. Common pretexts include:
- Invoice Scams: Posing as a vendor and sending a fake invoice for goods or services.
- Investment Scams: Promising lucrative returns on non-existent investments.
- Romance Scams: Building an online relationship and then fabricating a crisis or investment opportunity.
- CEO Fraud: Impersonating a company executive and requesting urgent wire transfers.
- Other Impersonations: Posing as a government official, tech support agent, or someone the victim knows and trusts.
Second, the fraudster must have access to a bank account where all payments are directed. This ‘mule account’ belongs to their accomplices or a third party to avoid direct identification of the perpetrator based on their account details.
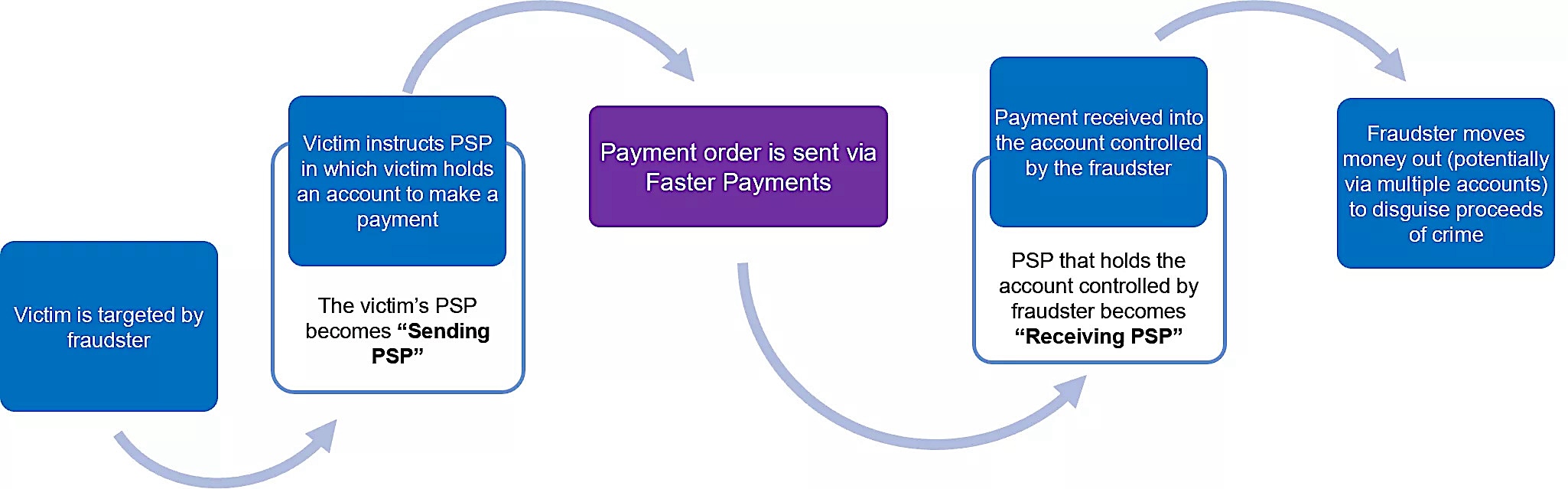
To activate the trap, the fraudster typically follows a five-step sequence:
1. Identifying Potential Victims
Fraudsters identify potential victims, often through public social media profiles, data breaches, or phishing campaigns.
2. Establishing Contact
To build rapport, the fraudster contacts the victims by presenting the bogus offer through phishing emails, phone calls, text messages, or social media.
3. Follow-up and Building Urgency
When the potential victim responds positively, the fraudster follows up to build trust and create a sense of urgency, prompting quick action for payment.
4. Initiating the Payment
Once the victim is convinced that the pretext is real, the fraudster offers guidance on the payment process until it is completed.
5. Funds Interception and Cleanup
After the victim authorizes and sends the payment, the fraudster quickly transfers the funds to multiple accounts or withdraws it as cash to obscure the money trail. Next, they delete their fake identities and all correspondence with victims.
Types of APP Fraud
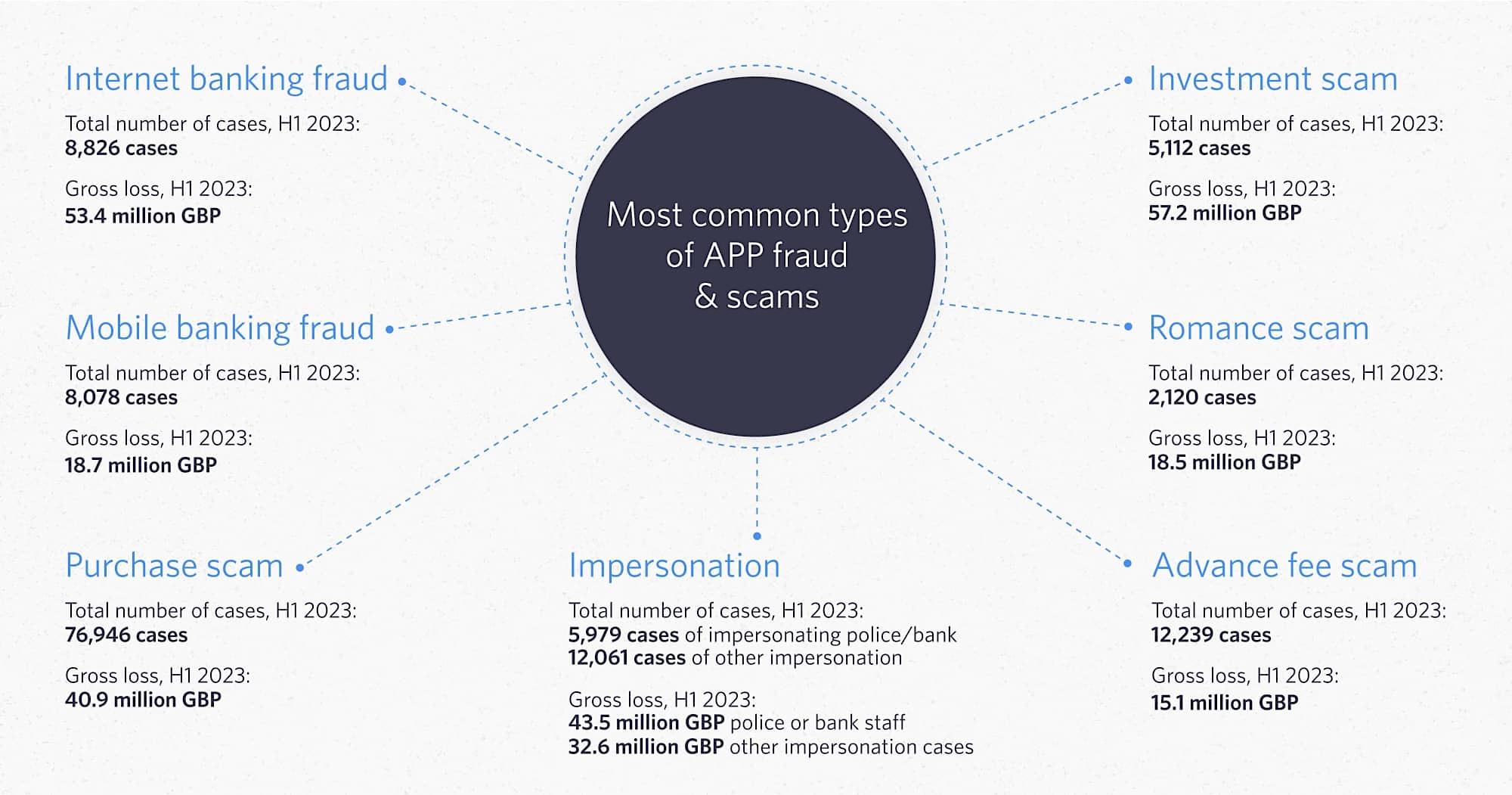
Most categorizations of APP fraud focus on the pretext of impersonation used in each type of APP scam. For example, an ‘Invoice Scam’ is when scammers pose as a trusted supplier requesting payment, and a ‘Romance Scam’ is when scammers pose as a romantic partner needing financial help.
However, since all APP fraud relies on digital payment infrastructure, another option is to categorize them based on the three most common types of payment initiation:
APP Fraud via Website Impersonation
In this case, APP fraud is committed by enticing the victim to visit a phony website impersonating a legitimate business’s site. These spoofed websites have the exact look and feel of the authentic site, complete with a fully functional payment gateway to trick unsuspecting victims into making payments to the fraudster.
APP Fraud via Mobile Payment Apps
This is another common form of APP fraud, in which the fraudster convinces the victim to transfer money using a mobile payment app. Payment apps offer a fast, easy way to send funds, making them attractive targets for scammers.
APP Fraud via Third-party Payment Gateways
In this scenario, the fraudster provides the victim with a payment link that directs them to a legitimate-looking payment gateway. The victim initiates the payment through their bank account or credit card, unknowingly sending funds to the fraudster’s account. This method can also lead to an Account Takeover (ATO), where the fraudster gains access to the victim’s online banking credentials.
6 Steps to Prevent APP Fraud
APP fraud isn’t just about financial loss; it’s a multi-pronged attack that can severely damage a company’s reputation and erode customer trust. To safeguard your business and customers, consider these six essential steps for preventing APP fraud:
1. Protect Customers in Real-time Against Website Impersonation
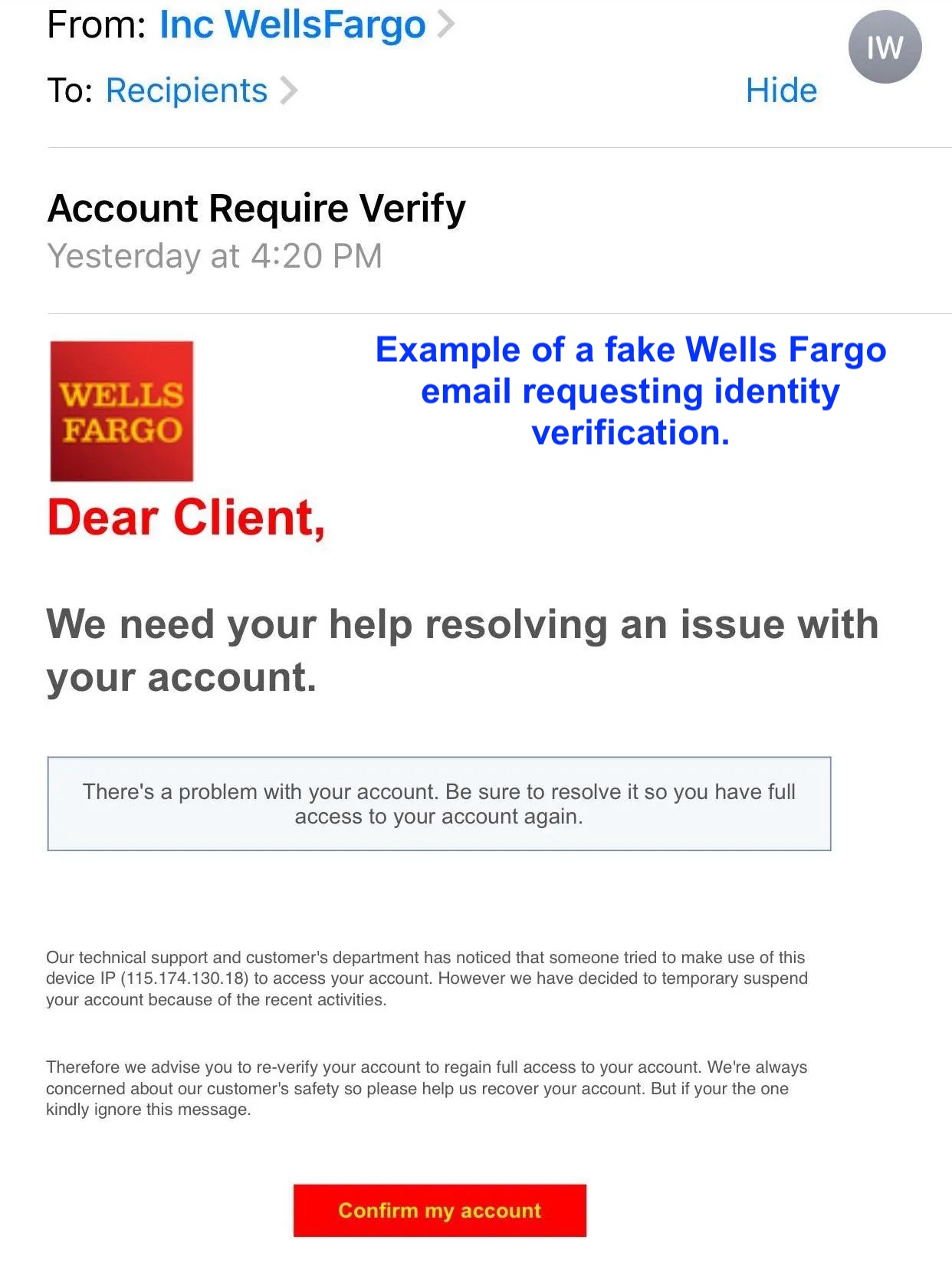
Even the most devastating APP scams often use simple phishing-related techniques to lure victims to fake websites identical to those being impersonated.
While fake sites aren’t new, their success as part of APP scams is growing, partly thanks to how easy it now is to generate highly realistic phishing pages and scam emails using Generative AI.
The challenge for businesses? How do you protect the most vulnerable customers when even the most ‘scam aware’ customers fall for APP scams involving fake websites? The answer is active, real-time protection.
Through its real-time digital risk protection solutions, Memcyco actively protects customers from APP scams involving phishing-related digital impersonation techniques.
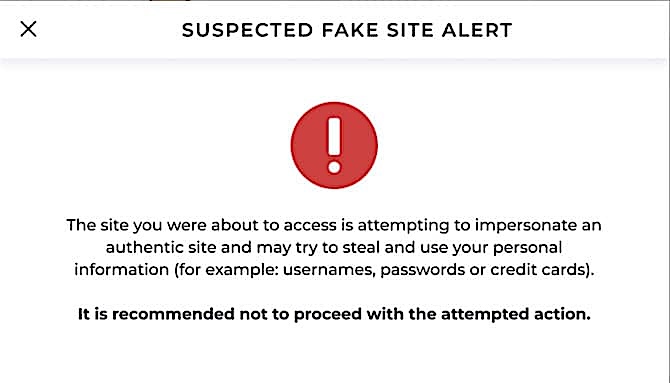
When a customer tries to access a fake site via a phishing or ‘smishing’ link, Memcyco’s technology instantly detects the click. The company is immediately notified of the attack details, including the domain, attack time, and customer information, enabling immediate protective actions.
Additionally, customers receive a Red Alert displayed via the fake site itself, warning them to turn back. If they ignore this warning and proceed, any sensitive data they may expose (like user credentials or card data) is replaced with artificial, marked data that can be tracked if used by the attackers.
This comprehensive strategy allows Memcyco to effectively stop malefactors from using malicious websites to deceive customers into APP fraud.
2. Employ Robust Transaction Monitoring and Verification
Implementing a multi-layered approach to transaction monitoring is essential for detecting and preventing APP fraud. This approach includes:
- Rule-Based Systems: These systems flag transactions that deviate from established patterns, such as unusual amounts or new recipients.
- Machine Learning: Leveraging machine learning algorithms can detect fraud patterns and subtle anomalies that traditional systems might miss.
- Human Review: Flagged transactions should undergo human review to confirm or deny fraudulent activity, ensuring an additional layer of scrutiny.
- Additional Verification: Companies must require additional verification methods such as out-of-band confirmation (e.g., phone calls or text messages) or biometric authentication for high-risk transactions.
This multi-faceted approach helps identify and address suspicious transactions before any damage occurs.
3. Bolster Email Security Measures
Fraudsters use various techniques to create fake email addresses, making sender verification crucial. Verifying the legitimacy of an email domain and flagging fraudulent addresses can be done at both the email service provider and end-user email client levels.
Email service providers track email domain reputation scores based on factors like delivery success rates, bounce rates, and spam complaints. On the user side, email clients offer spam filters and visible cues to help differentiate genuine emails from fraudulent ones, enhancing protection against email-based APP fraud.
4. Leverage AI to Monitor Social Media
Social media has become a popular platform for addressing customer complaints, providing another avenue for fraudsters to impersonate businesses and extract personal information. That’s why monitoring social media conversations is crucial for identifying and preventing app fraud.
AI tools can efficiently scale these operations by analyzing social media data and messages. Combined with human oversight, they provide dual-layer monitoring for potential fraudulent conversations. This proactive approach helps detect and mitigate APP fraud attempts initiated through social media.
5. Enforce Strict Controls for Business Accounts
In some cases, APP fraud leads to malefactors from outside or even inside the organization gaining unauthorized access to internal systems to scam customers. This can lead to an Account Takeover (ATO) where the compromised account is exploited for further fraud.
To prevent these incidents, companies must enforce robust security measures, including:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Ensure that access to IT systems requires multiple levels of verification.
- Dual Control Accounts: Implement the maker-checker principle, where one employee (the maker) initiates a transaction, and another (the checker) verifies and approves it to authorize transactions.
- Strict Protocols for Urgent Requests: Manage exceptional requests with stringent verification processes.
- Regular User Access Reviews: Conduct periodic user access reviews of privileges to ensure that employees have the appropriate access level for their roles and that any unnecessary permissions are revoked.
These measures help secure internal systems and prevent insider-initiated APP fraud.
6. Implement Strong Customer Authentication, Education, and Reporting
Businesses must implement robust customer authentication, continuous education, and efficient reporting processes to combat APP fraud effectively. Here’s how:
Advanced Authentication Methods
Enhance security for online banking and payment platforms by deploying multi-factor authentication (MFA) and/or other, more advanced authentication methods:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require multiple forms of verification, such as passwords and one-time codes.
- Biometric Authentication: Verify users with fingerprint, facial recognition, or voice identification.
- Behavioral Biometrics: To detect anomalies and analyze user behaviors, such as typing patterns and mouse movements.
Customer Education
Educate customers about APP fraud risks and prevention tips through:
- Clear Communication: Provide straightforward information on your website and in transaction confirmations.
- Regular Security Alerts: To inform customers about potential threats, send frequent alerts via email, SMS, or push notifications.
- Interactive Resources: Use quizzes, videos, or webinars to enhance understanding of APP fraud and prevention methods.
Active Reporting Systems
Encourage customers to report fraudulent incidents by implementing the following:
- Active Customer Touchpoints: Regularly inform customers about APP fraud and its risks.
- Awareness Campaigns: Educate customers on common fraud techniques and recognition tips.
- Regular Communication: Send checklists via email or messages to help customers identify potential APP fraud by asking simple questions, such as:
- What is the reason for the money transfer?
- How well do they know the recipient?
- What are the verifiable identity and contact details of the recipient?
By integrating strong customer authentication, continuous education, and a robust reporting system, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of APP fraud—and empower their customers to protect themselves. Each of these six steps plays a critical role in mitigating the risks associated with APP fraud, helping companies safeguard their financial transactions while bolstering trust in digital payment systems.
Stop Customers from Falling for APP Scams with Memcyco’s Real-Time Protection
APP fraud relies on social engineering tactics that trick victims into initiating authorized payments to fraudulent accounts, such as phishing emails with spoofed sender addresses. Memcyco makes it harder for scammers to create convincing fake websites used in phishing attacks by protecting against website spoofing while keeping customers and their data continually protected in real-time.
Memcyco’s digital risk protection solutions offer businesses comprehensive visibility and control over phishing-related digital impersonation fraud, preventing account takeover (ATO), financial theft, data breaches, and ransomware attacks. In addition, Memcyco uses proprietary ‘nano defender’ technology that proactively detects, protects, and responds to website impersonation attacks in real-time.
Schedule a Memcyco demo to discover how Memcyco keeps customers and revenue safer from the threat of APP fraud.